Papilloma is a lesion of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the human papillomavirus virus.
Causative agents - viruses of the genus Papilloma virus. Currently, more than 60 versions are known, 32 of which are known to cause disease.Transmission routes - contact (via skin microtrauma), genitals, perinatal (during childbirth.
Manifestations of papillomas
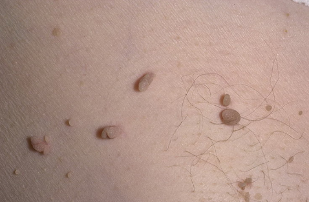
- Pulmonary papillomas (warts).
Hands, and less often other parts of the body, are often observed. Local lesions are common in children and adolescents. In immunized patients, wart lesions can be widespread. The incubation period is 1-6 months. The maximum number of viruses is observed in the affected tissues 6 months after infection. - Papillomas Vulgar (simple).
Their causative agent is the human papillomavirus (HPV) virus. This shape is represented by hard lumps with a rough surface 1 mm in diameter or more, with a tendency to merge. Vulnerable papillomas often cover a large area. They can be seen anywhere, but are more often located on the back of the palms and fingers, in children - on the knees. An individual papilloma can last for several months or even years, practically unchanged, but the process can also spread quickly. Isolated cases of papilloma degradation are a tumor. Immune-deficient states contribute to the spread of the process. - Plantar Papntaromas.
The causative agent is HPV-1 (deep form), HPV-2 (mosaic warts) and HPV-4 (minor lesions). The process begins with the appearance of a small shiny bump, acquiring typical papilloma characteristics, surrounded by a protruding edge. Sometimes, around one papilloma, many daughter formations appear, like bubbles - mosaic warts.
Plantar papillomas can be painful and make walking difficult. Their lifespan is different. In some cases, especially in children, any number of papillomas can disappear spontaneously. This form of the disease is often confused with calluses that appear in places of pressure on the fingers or between the fingers. Corns, unlike papillomas, have a smooth surface with a skin pattern. - Flat papillomas.
Their causative agent is HPV-3 and HPV-10. They are indicated by smooth lumps of normal skin color (light yellow or slightly colored). They can be round or polygonal in shape. The appearance of flat papillomas is usually accompanied by itching, inflammation in the affected area, redness, salivation, mainly in children. - Filiform papillomas.
They are found in 50% of the population over the age of 50 more often in the amputations, in the scalp, on the neck, around the eyes. The process begins with the appearance of small yellow or slightly colored cones, then enlarged and turned into elongated dense elastic formations up to 5-6 mm in size. In areas of possible trauma, papillomas can become inflamed. Their event does not occur spontaneously. - Local epithelial hyperplasia (Beck's disease).
The causative agents are human papillomaviruses 13 and 32. The disease was first described in American Indians. The mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, lips were observed in the form of small papillary eminences merging. - genital warts.
The causative agents of genital warts are human papillomaviruses with low (6, 11), medium (31, 33, 35) and high (16, 18) oncological risk. Viruses are sexually transmitted. The incubation period lasts from several weeks to months. In some cases, the lesions are minimal, often unnoticed. Infected cells are prone to malignant degradation. In most cases, a state of immunodeficiency is accompanied by a long and widespread process.
Cervical cancer is usually diagnosed in women with genital warts. In most cases, regardless of the age of the patients, DNA hybridization of the viral genome is detected. The causative agent is HPV-18. - Juvenile papillomatosis of the larynx.
The causative agents are HPV-6 and HPV-11. They are rarely registered. In most cases, papillomatosis is found in infants under 5 years of age who are infected in the mother’s birth canal. The appearance of characteristic growth of the vocal cords is noted, leading to speech difficulties and impaired air circulation in the upper respiratory tract.
Treatment of papillomas
The same symptoms can be symptoms of different diseases, and the disease may not progress according to the textbook. Don't try to cure yourself - consult your doctor.
Currently, there is no agreed international standard for the treatment of papillomas. The official treatment guidelines to date include
- Cytatatics
- (antineoplastic drugs), laser cryo
- , Electro deletion
- .
But they are not always effective and are accompanied by relapses.
Other treatments for papillomas:
- For isolated and occasional (simple) papillomas - surgical removal (crystallization, laser removal in combination with immunity correction).
- For plantar - cryodestruction, laser and / or diathermocoagulation.
- Mosaic papillomas are the most difficult to treat. When they disappear, especially in children, signs of inflammation are noticed.
- For flat forms - cryotherapy with immunity correction.
- For filiform - diathermocoagulation.
- For local epithelial hyperplasia, cryotherapy with immunity correction.
- For warty pulmonary dysplasia, cryotherapy or diathermocoagulation with subsequent correction of immunity.
- In genital warts - removal of warts with cryo therapy, laser excision or diathermocoagulation and mandatory correction of the immune system.
Treatment of genital papillomas can be difficult with other genital infections (chlamydia, bacterial vaginosis, herpes, CMV infection, etc. ). In these cases, treatment is performed in parallel.















































































